As modern energy grids evolve from one-way power flow to two-way, dynamic, and smart grid structures, the backbone of this transformation is formed by communication protocols. In a Substation Automation project, the conversion of physical quantities in the field (current, voltage, circuit breaker status, etc.) into digital data and its transfer to the control center is directly related to the capabilities of the selected protocol.
Today, there are three main protocol families that have become industry standards: IEC 60870-5 series, DNP3, and IEC 61850. In this article, we will deeply examine the technical architectures of these protocols, their advantages over each other, and how the correct protocol selection should be made in Substation SCADA projects, from the perspective of Mikrodev RTU and automation solutions.
The Evolution of Communication in Energy Automation
In conventional substations (conventional systems), protection and control were performed via analog signals and dry contacts carried by thousands of meters of copper cable. This structure was a difficult-to-maintain, costly-to-expand, and complex-to-diagnose fault system.
With digitalization, Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) came into play. Protection relays, energy analyzers, and RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) have now become communicating computers. However, the necessity for these devices to “speak the same language” created the need for standardization. This is where IEC and IEEE standards came in.
The Standard of Telecontrol: IEC 60870-5
The IEC 60870 standards, developed by the European-based IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), are specifically designed for telecontrol (remote supervision) systems. This is the standard widely used by TEİAŞ (Turkish Electricity Transmission Co.) and distribution companies in Turkey.
IEC 60870-5-101 (Serial Communication)
Defines communication over serial ports (RS232/RS485). It can operate at low bandwidth but is limited to point-to-point or multidrop structures. Today, it is being replaced by its TCP/IP-based version in modern projects, but it is still actively used in legacy systems.
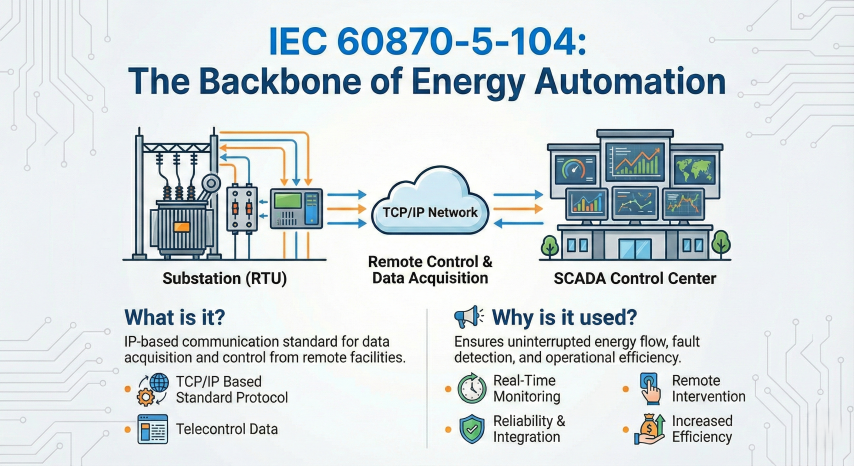
IEC 60870-5-104 (TCP/IP Communication)
It takes the application layer of IEC 101 and wraps it into TCP/IP packets at the transport layer. This enables data transmission over Ethernet networks, Fiber Optic infrastructures, and 4G/LTE modems.
Technical Features and Advantages:
- Event-Driven Transmission: Instead of continuous polling, data is only sent when it changes (e.g., when a circuit breaker opens). This utilizes bandwidth efficiently.
- Time Stamping: The time of occurrence of events is recorded with millisecond accuracy. This is critical for post-mortem analysis.
- Buffering: When communication is lost, devices like Mikrodev RTU300 store the data in their internal memory and transmit it to the center retroactively when the connection is restored.
North America’s Choice: DNP3 (Distributed Network Protocol)
DNP3 is an open protocol initially developed for the electric and water sectors, standardized especially in North America. Although it serves similar purposes to IEC 60870, it has some structural superiorities.
Why DNP3?
- Fragmentation: DNP3 can divide large data packets into smaller pieces for transmission. This increases transmission success over noisy and low-quality lines.
- Classification (Class 0, 1, 2, 3): Data is categorized by priority. Critical alarms (Class 1) can be sent before normal measurements (Class 3).
- Unsolicited Responses: The Slave device (RTU) can spontaneously send data when an important event occurs, without waiting for the Master to query.
DNP3, which is frequently encountered in water and wastewater projects, is also preferred in Energy Transmission Automation projects, especially in challenging field conditions.
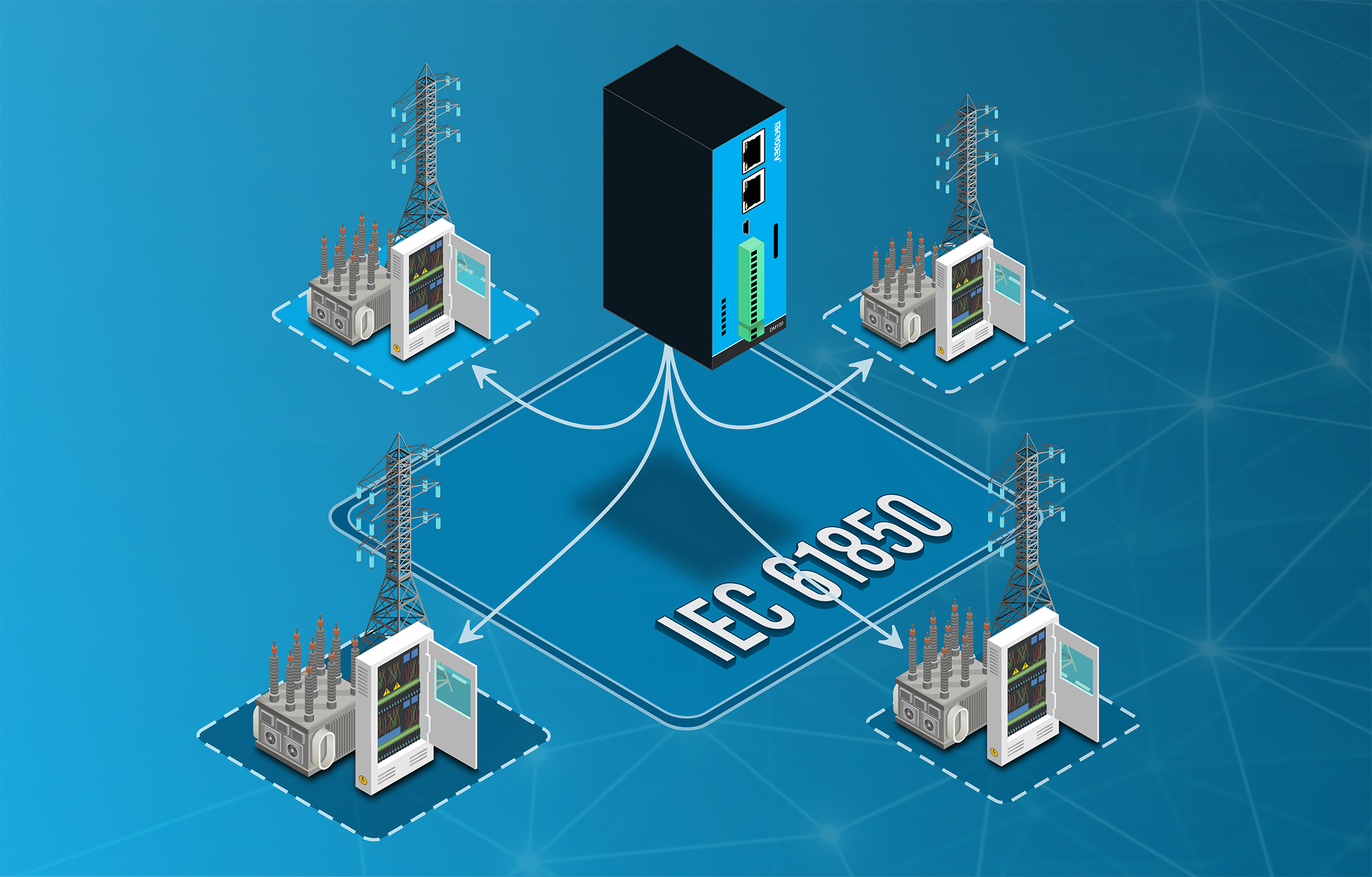
The Game Changer: IEC 61850
IEC 61850 is not just a protocol but a comprehensive engineering and communication standard for substations. Unlike other protocols, it adopts the philosophy of “replacing wires with communication.”
Key Differences:
- Object-Oriented Modeling: A circuit breaker is not just a “bit”; it is an object defined by its status, health, and number of operations under the “XCBR” logical node.
- SCL (Substation Configuration Language): System configuration is done with XML-based files (SCL, ICD, SCD). This ensures that different brands (Mikrodev, Siemens, ABB, etc.) recognize each other (Interoperability).
IEC 61850 Sub-Protocols: GOOSE and MMS
In a Substation Automation project, IEC 61850 operates at two main levels:
- MMS (Manufacturing Message Specification): This is vertical communication. It is used for data transfer from IEDs (Relays, RTUs) to the SCADA center (e.g., ViewPLUS SCADA). It works with a Reporting mechanism.
- GOOSE (Generic Object Oriented Substation Event): This is horizontal communication. It is very fast communication (< 4ms) between two protection relays or a relay and an RTU, without going through the SCADA.
- Example: When the protection relay at the transformer inlet sees a fault, it sends a “Trip” command to the other relay at the feeder outlet not via a copper cable, but via an Ethernet network using a GOOSE message.
Protocol Selection Criteria in Substation SCADA Projects
The following matrix should be considered when deciding which protocol to use in a project:
| Criteria | IEC 60870-5-104 | DNP3 | IEC 61850 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area of Use | WAN (Wide Area Network) | WAN / LAN | LAN (Local Area Network) |
| Communication Direction | RTU -> Control Center (NCC) | RTU -> NCC | Device -> Device & Device -> SCADA |
| Data Structure | Point List | Index-Based | Object-Oriented (Logical Nodes) |
| Bandwidth Need | Low | Low | High (Especially for GOOSE/SV) |
| Setup Complexity | Low | Medium | High (Requires Engineering) |
| Time Synchronization | Available | Available | Very Precise (SNTP/PTP) |
Hybrid Architectures and Gateway Requirement
In the real world, a substation is rarely established with a single protocol. Hybrid structures are generally seen:
- The relays within the site communicate with each other using IEC 61850 (GOOSE).
- Data is collected in a Data Concentrator.
- The collected data is sent to the upper-level (Load Dispatch) SCADA system via IEC 60870-5-104.
This is where the “Multiprotocol” capability of Mikrodev RTU devices becomes vital. A Mikrodev device can simultaneously:
- Read energy analyzers over Modbus TCP/RTU.
- Pull data from protection relays as an IEC 61850 Client.
- Present this collected data to the TEİAŞ or EDAŞ center as an IEC 60870-5-104 Slave.
- Push the same data to a cloud platform or mobile monitoring application via MQTT.
Protection Relay Communication and RTU Integration
Protection relay communication is the most critical part of the system. Relays are not just devices that operate during a fault; they are sources that constantly produce data about the grid quality (Harmonics, Sag/Swell events).
In old systems, only “Opened/Closed” information was received from the relays, whereas in modern Substation SCADA systems, oscillographic fault records (Disturbance Records) are also retrieved from the relays. These records are used to understand the cause of the fault (lightning strike, line break, insulation fault, etc.).
The Mikrodev RTU product family has libraries that can communicate with different brands of protection relays (Siemens, Schneider, ABB, GE, etc.) both over serial ports (IEC 101, Modbus) and over Ethernet (IEC 104, IEC 61850). This allows for the creation of “Vendor Independent” solutions.
Future Trends: IoT and Big Data
In addition to IEC 61850 and classic SCADA protocols, IoT protocols have also started to enter substations. Light protocols like MQTT or CoAP are used, especially for monitoring non-operational data such as transformer oil temperatures, ambient humidity, and door security.
Mikrodev’s IoT Gateway Solutions can carry this data to cloud-based analysis platforms over a parallel line, without burdening classic SCADA traffic. This enables the execution of “Predictive Maintenance” algorithms.
Correct Integration, Secure Energy
In Substation SCADA projects, protocol selection is not just a technical choice but a strategic decision that affects operating costs and system security.
- For fast and smart on-site automation: IEC 61850.
- For stable and standard remote monitoring: IEC 60870-5-104.
- For harsh and low-bandwidth lines: DNP3.
The most successful projects are those that position each of these protocols according to their strengths and ensure integration with flexible, powerful, and local hardware/software solutions like Mikrodev. Energy transmission automation is rapidly advancing toward a future where fiber optics and smart algorithms replace copper cables.