The management, distribution, and wastewater treatment processes of water resources have evolved from manual controls to fully automated, intelligent systems. At the heart of this transformation are Water SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems and RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) architecture, which act as our eyes and ears in the field.
In this article, we will examine how a modern water automation infrastructure should be designed, the importance of industrial protocols such as IEC60870, and the critical components in Water and Wastewater Automation processes.
Water SCADA: The Digital Twin of Water
A Water SCADA system is a centralized software platform that enables monitoring and control of a water network spread across a wide geographical area from a single center. For a municipal water authority or a treatment plant, SCADA visualizes all data in real time—from pump statuses and reservoir levels to chlorine ratios and pipeline pressures.
Unlike traditional systems, a modern SCADA Water Application focuses on reducing water loss and leakage rates and increasing energy efficiency through big data analytics.
The Brain in the Field: RTU (Remote Terminal Unit)
No matter how powerful the central SCADA software is, the accuracy and continuity of data coming from the field are essential. This is where the RTU comes into play.
RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) devices are industrial control units installed at remote locations such as pump stations, water reservoirs, or valve chambers, designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Unlike PLCs, RTUs are designed to communicate over wide-area networks (GSM/GPRS, Radio Modem, etc.).
An RTU converts analog data received from sensors (e.g., water level) into digital data and transmits it to the center, and manages field devices based on commands received from the center (e.g., stop the pump). Programmable RTU solutions developed by Mikrodev feature “Data Logging” capabilities to prevent data loss even during intermittent network connections.
Critical Communication Protocols: IEC60870 and DNP3
In water and wastewater automation, transmitting data securely and with time stamps is of vital importance. While the standard Modbus protocol is sufficient for simple applications, international telemetry standards are preferred for critical infrastructures.
IEC60870-5-101/104: This protocol, commonly used in systems spread over wide geographical areas, ensures data integrity. Mikrodev RTU devices provide uninterrupted data flow in local and global projects with IEC60870 support.
DNP3 (Distributed Network Protocol): Another powerful protocol frequently used in the water sector, enabling event-driven data transmission.
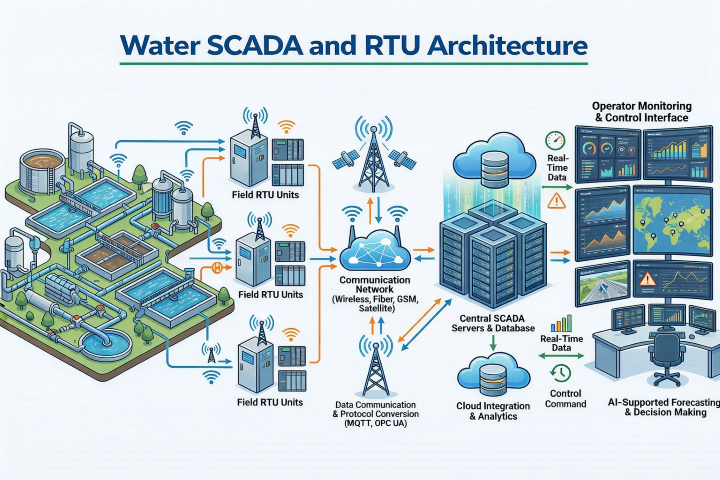
Example System Architecture
An ideal water automation architecture consists of three main layers:
Field Layer: Level sensors, flow meters, and motor drives.
Control and Transmission Layer (RTU): Devices such as Mikrodev RTU300 that collect data, execute local logic, and transmit information to the center.
Central Monitoring Layer (SCADA): ViewPLUS SCADA software, where data is processed and operators manage the system.
Why Mikrodev Solutions?
Preferred by many water authorities in Türkiye and around the world, Mikrodev products offer the following advantages in Water and Wastewater Automation projects:
Flexible Programming: Programmability in accordance with the IEC 61131-3 standard.
Wide Protocol Support: Modbus, IEC 60870-5-104, DNP3, and MQTT (IoT) support in a single device.
GSM/GPRS Integration: Built-in modem enables cloud or server connectivity without the need for additional hardware.
Establishing the right hardware and software architecture for efficient water resource management means not only saving today, but also securing the future.